Uninterruptible Power Supplies FAQ
Dive into the intricacies of uninterruptible power supplies with these FAQs.
Uninterruptible Power Supplies FAQ
Dive into the intricacies of uninterruptible power supplies with these FAQs.
A UPS is a backup power system that provides protection to the connected loads in case of utility power loss. This is achieved by providing power from an alternate source – such as batteries – for a pre-determined time until either the utility power returns or the facility can switch to another source such as a generator.
A UPS provides clean and uninterrupted power to your critical load, regardless of the state of the incoming power. Even if there is a complete loss of power to your critical load, or merely a spike or sag in the power coming from your utility source, the UPS will correct the anomaly and provide clean, uninterrupted power to the critical load.
Learn more about why you may need a UPS with our “What is a UPS?” blog post.
The difference between a Single Phase and Three Phase UPS is what type of voltage system it is applied to. This is as simple as how many power wires are connected to the UPS.
Single phase
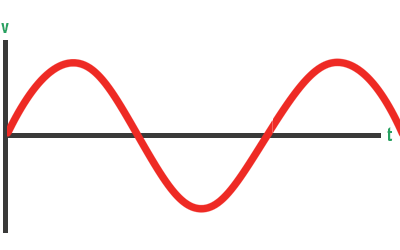
In a single phase UPS system, power flows through two wires – a power wire (phase) from the source to the load and returning via a neutral wire to the source. Graphically, this is depicted as a single sine wave. For example, appliances within homes or smaller commercial applications are powered by single phase power.
Typical voltages for single phase systems are 120V, 208V, or 240V depending on the region. Many single phase UPS systems are used for backing up individual computers, individual IT racks, or other applications with limited load (less than 10kVA).
3 phase
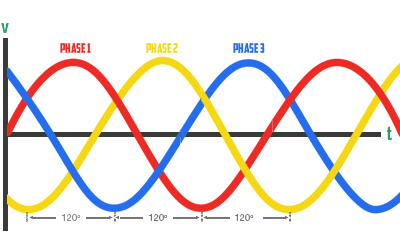
In a three phase UPS system, there are three power wires (phases) that each carry an alternating current of the same frequency and voltage. A three phase UPS may also have a fourth neutral wire, which is called a three phase, four wire UPS.
Graphically, this is depicted as three sine waves that are 120 degrees apart. Three phase power is most common for most loads higher than typical residential or small-scale commercial applications. Three phase UPS products typically go from 10kVA (approx.) to 2000kW.
The three most common types of static UPS systems are: Standby (offline), Line-Interactive, and Online Double Conversion. Learn more about the differences between the types of static UPS.
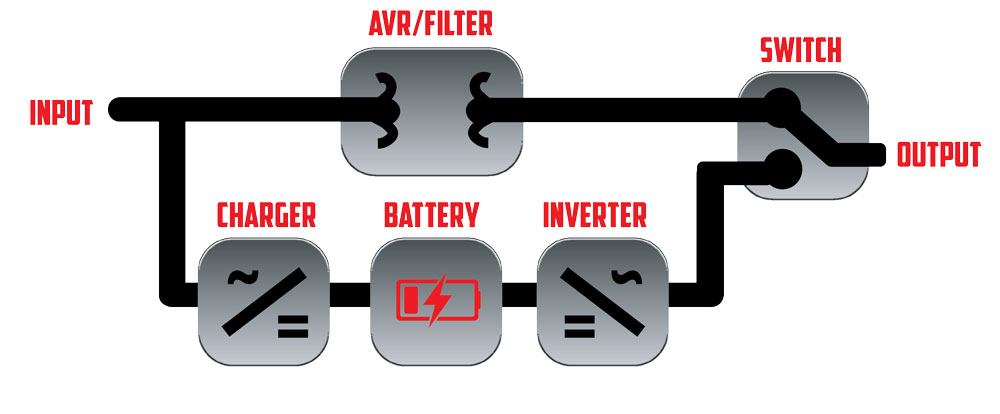
Double Conversion UPS
A double conversion UPS takes Alternating Current (AC) power, converts it to Direct Current (DC) power, and then back to AC.
This is a key process in power conditioning; providing clean power to the critical load and ensuring that all sags, swells, spikes, frequency variations, and line noise are removed from the current. Learn more about online double conversion UPS here.

Line Interactive UPS
A line interactive UPS will monitor the incoming voltage and either increase or decrease the output voltage using some form of voltage regulating transformer.
This provides the load with a minimal form of regulated power but does not protect against any frequency variation, high noise, or harmonics. Once the input voltage goes outside the range of regulation or the frequency goes outside a set range the UPS will switch to battery operation.
Depending on how advanced the line interactive UPS is it could either output a simulated sine wave (square wave) or an actual sine wave output.
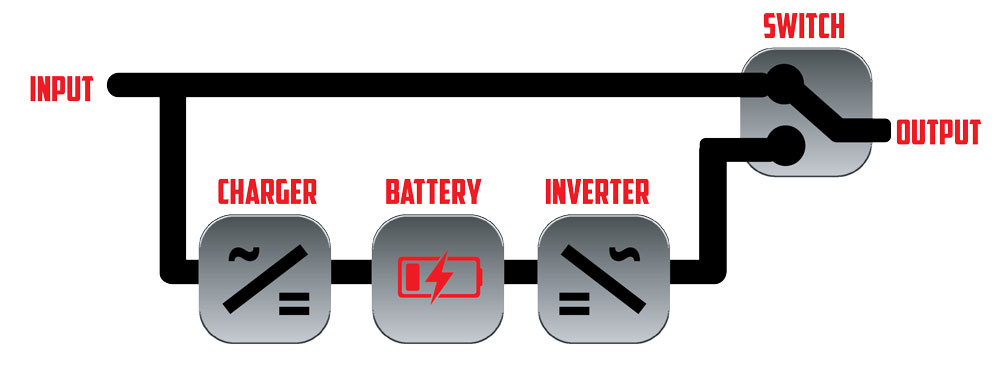
Standby (Offline) UPS
In a standby (offline) UPS, the load is directly connected to the utility voltage, and the UPS will only switch to battery operation in the event of a full utility outage or severe voltage sag.
These types of UPS provide no power conditioning or regulation for the output. These UPS are often used for desktop computers and other smaller kVA applications below 1kVA.
Redundancy in a UPS can refer to either internal module redundancy or system level redundancy.
- Internal redundancy is when there are additional power modules in a UPS that are available to carry the load in the case of a fault condition in another module.
- System level redundancy is when there are multiple UPS in a system that are available to carry the load in the case of a fault in an entire UPS.
Learn more about the types of redundant systems.
The efficiency of a UPS is the ratio of the output power to the input power and shows the internal losses of the system.
Calculation: Efficiency = (Output Power / Input Power) x 10
For example, if the output power of the UPS is 100kW and the input power is 103kW the resulting efficiency is 97%.
Mitsubishi Electric has multiple energy-efficient UPS products to support your critical load. Currently, our most energy-efficienct UPS is the SUMMIT Series® (500 & 750kVA).
Choosing the right size UPS is dependent on a variety of factors, from application to capacity needs, amongst others.
Our Product Manager of Engineered Solutions walks you through the basics of determining what size UPS is best to support your critical infrastructure.
- An internal bypass is located inside the UPS itself and provides an alternate path for power to flow, “bypassing” the power electronics. The internal bypass, however, does not isolate the entire UPS, and power is still present at the input and output connections.
- A maintenance bypass is an external piece of equipment, typically containing circuit breakers, that provides an alternate path for power to flow around the entire UPS. This allows you to remove power at the input and output connections allowing technicians to safely perform work on the equipment.
In general, a UPS battery is an energy storage device that goes into effect when the critical utility power of a UPS system is offline. Then, the UPS switches to drawing power from the battery to keep critical loads online and running.
The UPS battery can be of a variety of DC technologies and/or energy storage devices, and it is a critical component of a UPS system.
Choosing a battery depends upon the UPS system’s specific use case. This use case depends on the technical, safety, and commercial requirements of the customer.
The required UPS battery runtime needed depends on the use case of the UPS system.
Traditional UPS battery runtimes range from 5 minutes to 30 minutes, depending on the power rating of the UPS loads and the overall use case.
Typically, a battery or energy storage device for UPS applications is used to keep power flowing to the downstream loads long enough for the overall system backup generators or alternative main power sources to come online.
Recently, the required battery runtimes seen in the industry have been reduced to 1-3 minutes due to the speed at which the newer generators can come online.
If the UPS system use case is for hospitals or emergency lighting, the necessary UPS battery system runtimes could be much longer, ranging from one hour or more in total runtime.
Mitsubishi Electric has been manufacturing precision-engineered, highly reliable uninterruptible power supplies since 1964 and delivering solutions to North America’s critical facilities since 1985.
Explore our wide variety of UPS products, ranging from 6-2000kVA.
Mitsubishi Electric delivers the highest reliability among backup power equipment suppliers. Our robust technology is designed to deliver continuous power in the most demanding environments. Our 9900 Series of UPS has a sustained load carrying capacity of 99.9995% of their actual operational history.
Here is how we calculate this figure:
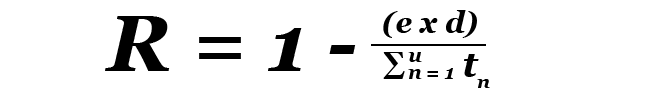
R = Mitsubishi Electric’s measure of reliability
e = Number of reported customer load loss events due to a Mitsubishi Electric UPS failure
d = Assumed maximum duration of load loss events
u = Number of Mitsubishi Electric uninterruptible power supplies shipped
tn = Assumed total available operational hours of UPS n since shipment
Learn more about Mitsubishi Electric reliability.
- Determine what voltage is available at the site.
- Determine what size UPS would be required.
Once that information is known, you can contact Mitsubishi Electric or see the different models and sizes of Mitsubishi Electric UPS.
Mitsubishi Electric’s Uninterruptible Power Supplies are online double conversion.
Learn the differences between an online double conversion UPS and a line-interactive UPS.
Yes! Mitsubishi Electric offers demonstration testing and factory witness testing in our Factory & Test Lab in Warrendale, PA.
Learn more about the importance of factory witness testing and UPS testing in general.
Please contact us to inquire about UPS testing.
Mitsubishi Electric UPS products are highly efficient, with models reaching up to 98% efficiency.
The 9900AEGIS and SUMMIT Series® UPS are ENERGY STAR certified, making them a great choice when looking for an energy-efficient UPS.
See how USCellular saw “substantial savings” by deploying our SUMMIT Series® UPS!
Below is a list of each current Mitsubishi Electric UPS products and its corresponding list of compatible battery chemistries:
| Mitsubishi Electric UPS | Battery Types | |||
| Lithium-Ion | VRLA | VRLA Pure Lead | VLA | |
| 9900D (1200-2000kVA) | X | X | X | X |
| 9900CX (1050kVA) | X | X | X | X |
| SUMMIT Series® (500 & 750kVA) | X | X | X | X |
| 9900B (300-750kVA) | X | X | X | X |
| 9900AEGIS (80-225kVA) | X | X | X | X |
| 1100B (10-80kVA) | X | X | X | |
| 1100A (10-50kVA) | X | X | ||
| 7011B (6-12kVA) | X | X | ||
Yes! The 1100 Series (10-80kVA) and the 9900D (1200-2000kVA) are both modular and expandable.
Mitsubishi Electric offers UPS systems from 6kVA (7011B) to 2000 kVA (9900D).
| Mitsubishi Electric UPS | kVA Range |
| 9900D | 1200, 1250, 1500, 1600, 2000 |
| 9900CX | 1050 |
| SUMMIT Series® | 500, 750 |
| 9900B | 300, 500, 750 |
| 9900AEGIS | 80, 100, 150, 160, 225 |
| 1100B | 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80 |
| 1100A | 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 |
| 7011B | 6, 8, 10, 12 |
Yes! Brochures, specifications, data sheets, outline drawings, owner’s manuals, and facility planning documents are all available on our website and organized by product line on each respective product page.
Explore all Technical Documents and Literature.
It is recommended to never run a UPS at 100% load capacity. Most are run at a 60-75% capacity. This can vary based on the design of the facility, type of load, and/or the redundancy of the system.
Learn more about the basics of UPS sizing.
The installation requirements vary depending on the UPS model.
Please refer to the specifications outlined in the owner’s manual for the applicable model, which can be found on the Technical Documents page or at the bottom of the respective UPS product page.
When you are preparing to have your UPS started up, you need to make sure to complete a Pre-Startup Checklist to verify everything is ready for the technician coming to site.
Putting a Mitsubishi Electric UPS into static bypass can vary between UPS models.
Please refer to specifications for your specific model, which can be found on the Technical Documents page or at the bottom of the respective UPS product page.
The overload capacity of a UPS will vary based on the product family and on the kVA of the specific unit.
Please refer to specifications for your specific model, which can be found on the Technical Documents page or at the bottom of the respective UPS product page.
How long your UPS system will run on battery is entirely dependent on your needs.
- For many applications, total runtime may be five minutes or less if a generator is utilized in your system.
- For applications in geographically dispersed locations (such as telecom towers), much longer runtimes may be necessary, extending to 30 minutes or longer.
- Other customers who do not wish to use a fossil fuel generator at all may opt to use a lithium-ion battery to replace the generator completely.
- 9900AEGIS: up to 4 units
- 9900B: up to 8 units
- SUMMIT Series®: up to 8 units
- 9900CX: up to 6 units
- 9900D: up to 6 units
Since Mitsubishi Electric locates the controls for paralleling inside the UPS, the minimum other pieces of equipment required are shielded Cat6 cables for communications and the paralleling cabinet, also know as a Critical Load Cabinet (CLC).
For more information, please refer to our Parallel UPS Solutions page. Our knowledgeable Project Application Engineering team can help you and your business with planning and system design – Contact us!
Typically, a Mitsubishi Electric UPS has a design life of approximately 15 years.
- Wondering whether you should repair, replace, or upgrade your UPS? Check out this quick read.
- Wondering whether you should replace lifecycle parts or the whole UPS system? This article is for you!
Please visit our Product Lifecycle & Support page for more information around supporting your UPS and when to replace it.